Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
The "oil premium" refers to the additional cost added to the price of crude oil due to various factors beyond the basic supply and demand dynamics. Several elements contribute to the determination of this premium:
1) Geopolitical Tensions: Any instability in oil-producing regions or geopolitical tensions that threaten oil supply can lead to a premium. Conflicts in major oil-producing countries or regions can disrupt production and transportation, causing prices to rise.
2) Supply Disruptions: Natural disasters, accidents, or technical issues in oil production facilities, pipelines, or refineries can limit the supply of oil, leading to a premium as markets react to the reduced availability.
3) Market Speculation: Investor perceptions and expectations about future oil supply and demand, driven by speculation on global economic trends, can influence oil prices. Speculative activities can amplify price movements, leading to a premium or discount.
4) OPEC Actions: Decisions made by the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) and its allies regarding production levels and quotas can impact oil prices. Production cuts or increases can lead to price changes, including a premium.
5) Global Economic Conditions: The health of the global economy affects oil demand. Economic growth or contraction in major consuming countries can influence the premium attached to oil prices.
6) Inventory Levels: Oil inventories, both globally and within specific regions, impact prices. Low inventory levels or unexpected inventory draws can drive prices up, leading to a premium.
7) Transportation and Infrastructure: Any disruptions or constraints in the transportation or infrastructure networks, such as congested shipping routes or inadequate storage facilities, can affect the premium by impacting the ease of getting oil to market.
8) Currency Fluctuations: Exchange rate fluctuations between major currencies and the currency used in oil transactions (usually the US dollar) can influence the price of oil for buyers using other currencies, impacting the perceived premium.
Understanding these factors and their interplay is crucial for assessing the elements contributing to the oil premium. However, it's essential to note that the premium can be volatile and influenced by a multitude of constantly changing variables within the global oil market.
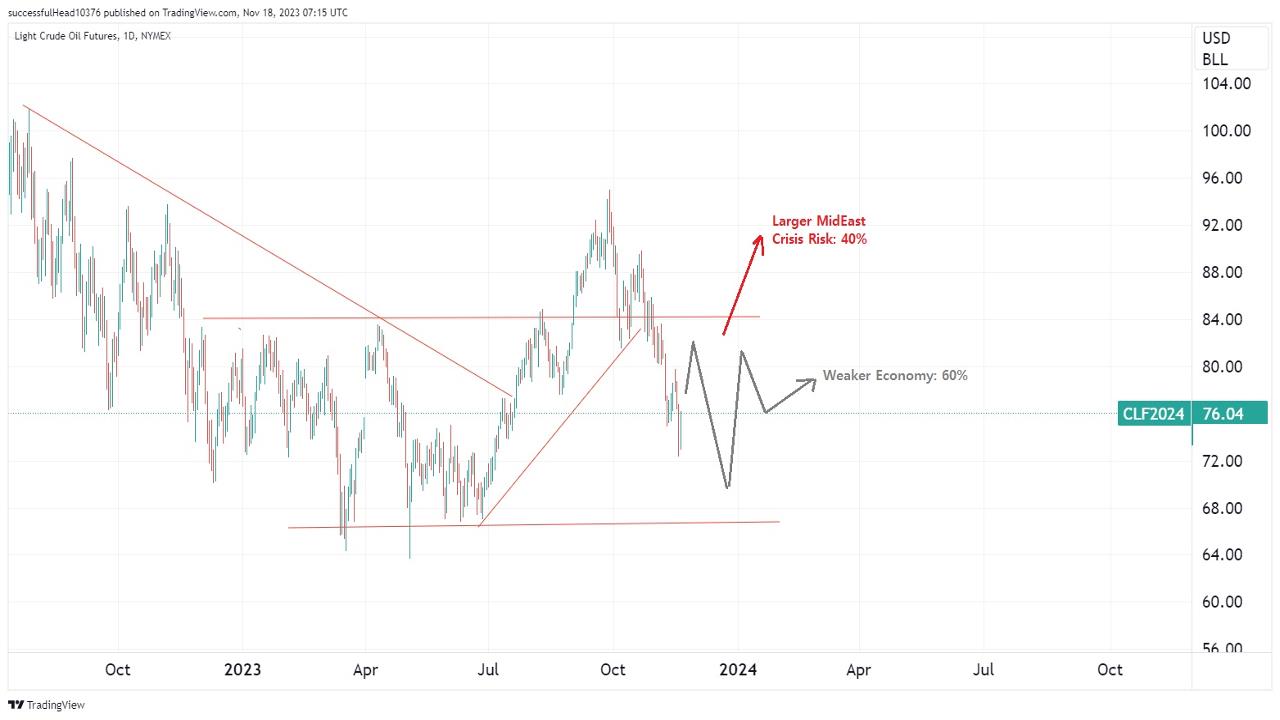
Chart:
References:


Comments