Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Predicting long-term weather conditions, especially for agricultural purposes, is a complex task due to the inherent variability and uncertainty in weather patterns. Here are some points to consider:
1) Accuracy: Long-term weather forecasting (beyond a few weeks or months) is inherently less accurate than short-term predictions. Weather models lose precision as the forecast period extends further into the future. While meteorologists use sophisticated models and historical data to make predictions, long-term accuracy diminishes due to the chaotic nature of the atmosphere and the numerous interacting factors involved.
2) Factors Affecting Predictions: Long-term weather forecasting for agriculture involves considering various climatic factors such as temperature, precipitation, humidity, wind patterns, and seasonal changes. Additionally, global climate phenomena like El Niño/La Niña, solar cycles, and atmospheric oscillations further complicate predictions.
3) Challenges in Agriculture: Farmers rely on weather forecasts to make critical decisions regarding planting, harvesting, irrigation, and pest control. Inaccurate long-term forecasts can lead to wrong decisions, impacting crop yields and farm profitability.
4) Technological Advances: Advancements in technology and data analytics have improved forecasting models and access to historical climate data. However, predicting weather trends beyond a few weeks with high accuracy remains challenging.
5) Risk Management: Farmers often use historical weather patterns, climate averages, and risk management strategies such as diversification of crops, soil conservation, and water management to mitigate the risks associated with uncertain long-term weather forecasts.
6) Regional Variations: Weather patterns vary greatly by region, making it even more challenging to make accurate long-term forecasts that cater to the specific needs of each agricultural area.
While long-term weather forecasts for farming present challenges, ongoing advancements in meteorological technology and improved understanding of climate patterns continue to enhance the accuracy of predictions. However, farmers often supplement these forecasts with traditional knowledge, experience, and adaptive practices to minimize the impact of unpredictable weather on their agricultural activities.
Chart:
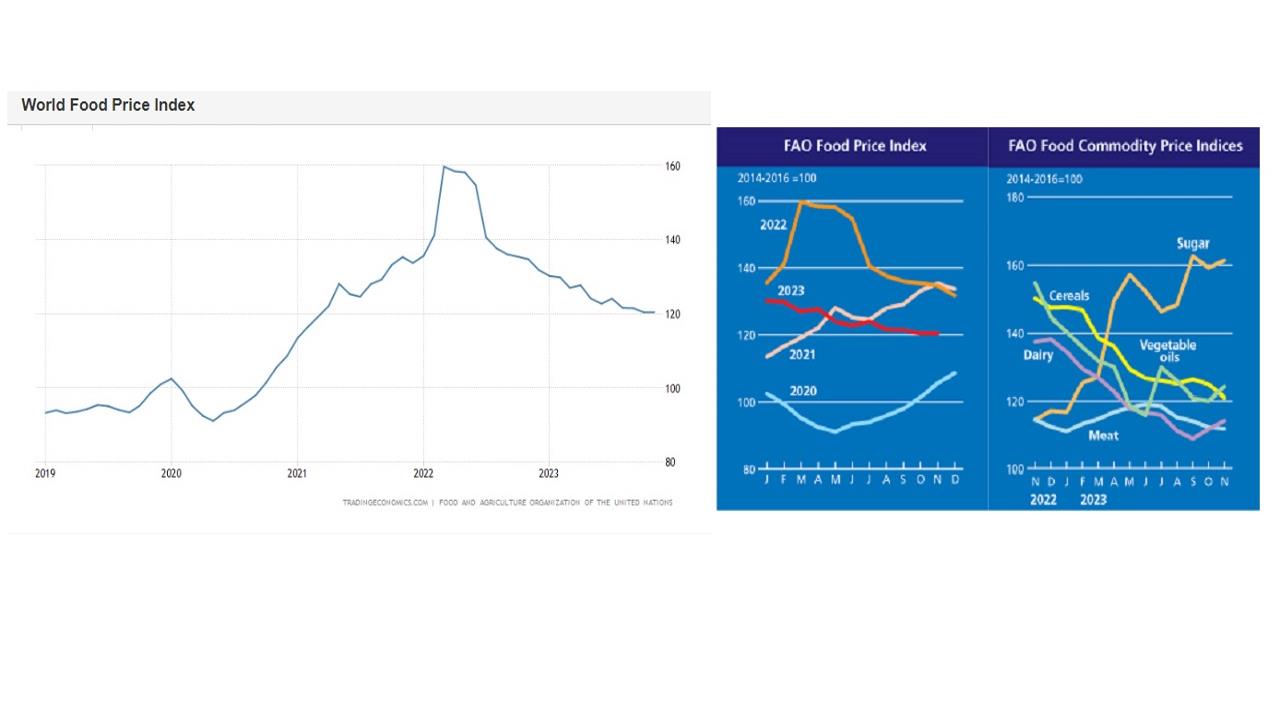
References:


Comments