Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Fertility rates, which measure the average number of children born to a woman during her reproductive years, can be influenced by a variety of factors. These factors can vary from one country or region to another, but some of the key factors that tend to impact fertility rates include:
1) Economic Development: As countries develop economically, fertility rates tend to decline. This is because in economically developed countries, there are greater opportunities for women to pursue education and careers, and there may be increased access to contraception and family planning services.
2) Education: Education, particularly for women, tends to delay childbearing and reduce fertility rates. Educated women often have fewer children and have them later in life, as they are more likely to prioritize career and personal development.
3) Access to Contraception and Family Planning Services: Availability and accessibility of contraception and family planning services can have a significant impact on fertility rates. When people have access to effective methods of birth control, they can make informed decisions about the timing and number of children they want to have.
4) Cultural and Religious Factors: Cultural and religious beliefs can strongly influence fertility rates. In some cultures and religions, larger families are encouraged or even considered a religious duty, leading to higher fertility rates. In contrast, other cultures may prioritize smaller families.
5) Government Policies: Government policies, such as pro-natalist policies that provide incentives for larger families, or policies that support work-family balance and gender equality, can influence fertility rates. For example, parental leave policies and affordable childcare can make it easier for couples to have children.
6) Social Norms and Peer Influence: Social norms and peer pressure can also play a role. When having fewer children becomes more socially acceptable or even fashionable, it can lead to a decrease in fertility rates.
7) Infant and Child Mortality Rates: In countries with high infant and child mortality rates, parents may have more children to compensate for the risk of losing some of them. As healthcare improves and child mortality rates decline, parents may feel more secure having fewer children.
8) Urbanization: Urbanization often leads to lower fertility rates. In urban areas, the cost of living is typically higher, and there may be less social pressure to have large families. Additionally, urban lifestyles often encourage delayed childbearing.
9) Economic Factors: Economic stability and job opportunities can influence fertility rates. In uncertain economic times, people may delay having children until they feel more financially secure.
10) Gender Equality: Greater gender equality can lead to lower fertility rates, as women have more control over their reproductive choices and may choose to have fewer children.
It's important to note that these factors can interact with and influence each other in complex ways, and the impact of these factors on fertility rates can vary widely from one population to another. Additionally, while these factors provide a general framework for understanding fertility trends, individual decisions about family size are highly personal and can be influenced by a wide range of individual circumstances and preferences.
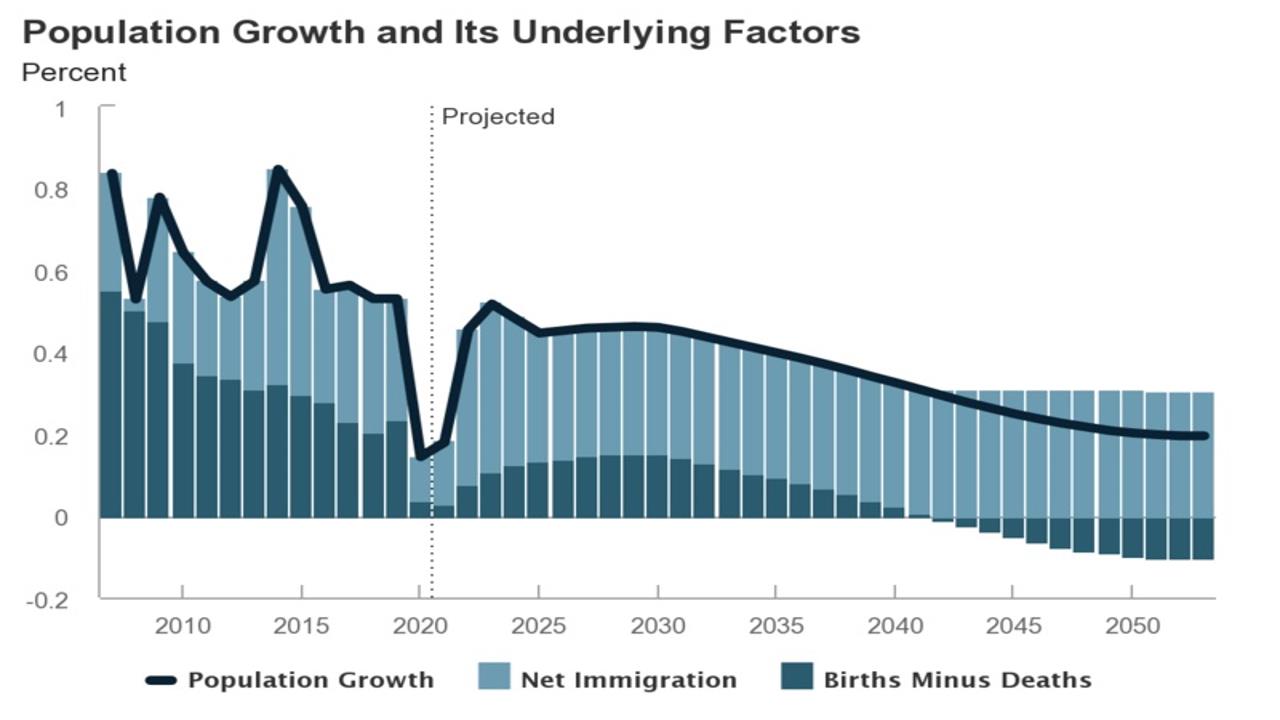
Chart:
References:


Comments