Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Martial law is a significant and rare event in the United States, typically declared in response to a severe emergency or crisis. When martial law is declared, the normal legal and civil processes are often suspended, and military authorities take control to maintain order and security. Here are the key attributes and implications of martial law:
1) Military Control: Martial law involves the transfer of authority from civilian institutions to military authorities. The military assumes control over law enforcement, government functions, and public order.
2) Suspension of Civil Rights: In practice, martial law can involve the suspension of certain civil rights and constitutional protections, such as freedom of assembly, freedom of speech, and protection from unreasonable searches and seizures. This is done to maintain order and security.
3) Curfews: Curfews are often imposed, restricting the movement of individuals during specific hours. Only authorized personnel, such as law enforcement and military, may be exempt from curfew restrictions.
4) Increased Security Measures: Martial law typically involves heightened security measures, including the deployment of military personnel, checkpoints, and increased surveillance. Individuals may be subject to search and identification checks.
5) Control of Communications: The government may control or limit the flow of information, including censorship of media and communication channels, to prevent the spread of information that could undermine the government's authority.
6) Control of Transportation: Martial law may include restrictions on the movement of vehicles and individuals, including the use of roadblocks and checkpoints. Travel may be limited to essential purposes.
7) Rationing of Resources: To manage scarce resources or maintain order, martial law can involve rationing of essential goods, such as food, water, and fuel.
8) Military Tribunals: Civil courts may be replaced by military tribunals or courts-martial. These military courts can handle legal matters, including criminal cases.
9) Restricted Civil Liberties: Martial law often results in a reduction of civil liberties and personal freedoms. It can be a challenging period for civil rights, and individuals may have limited legal recourse.
10) Declaration Process: The declaration of martial law typically requires formal action by the government or the president. The legal basis for martial law varies by country and is often defined in national or state laws.
11) Duration: Martial law is meant to be temporary and is lifted when the crisis or emergency situation has been resolved. However, the duration can vary, and its termination may depend on the judgment of the authorities involved.
12) Public Safety and Order: The primary goal of martial law is to restore and maintain public safety and order in times of extreme crisis, such as natural disasters, civil unrest, or war.
It's important to note that the declaration of martial law is a significant and controversial step in any democratic society. The decision to implement martial law is taken very seriously and is subject to legal and constitutional constraints. In the United States, the Posse Comitatus Act restricts the use of federal military personnel for law enforcement purposes within the country. Martial law should be an exceptional measure of last resort, used only in cases of extreme emergency when no other means can restore order and security.
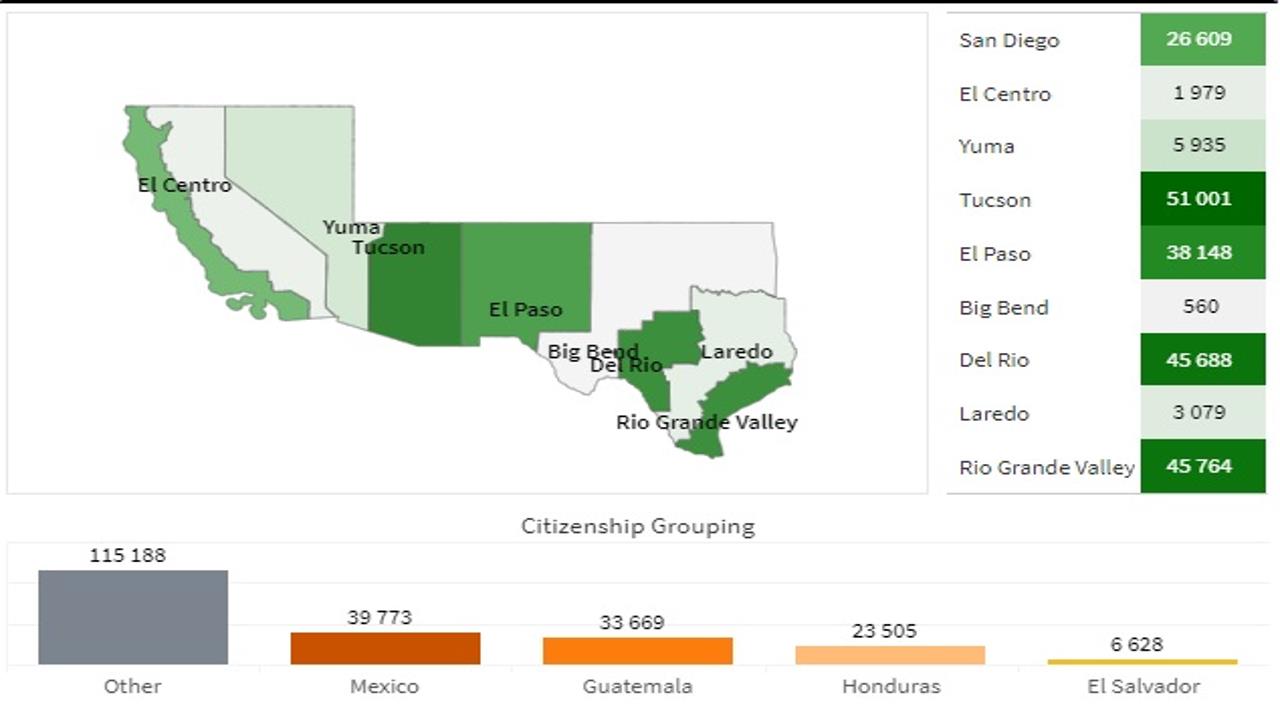
Chart:
References:


Comments