Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
The rise of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) in America can be attributed to several factors, which may vary in significance depending on the specific STD in question. Some key contributing factors include:
1) Decreased Awareness and Education: A lack of comprehensive sexual education and awareness about STDs can lead to risky sexual behaviors and unprotected sex.
2) Stigma and Shame: The stigma associated with STDs can discourage individuals from getting tested and treated, leading to the further spread of infections.
3) Decreased Condom Use: Inconsistent or reduced condom use, particularly among certain age groups, can increase the risk of transmission of STDs.
4) Alcohol and Drug Use: Substance use, including alcohol and drugs, can impair judgment and lead to risky sexual behaviors, increasing the likelihood of STD transmission.
5) Multiple Sexual Partners: Engaging in sexual activities with multiple partners without consistent and proper protection can heighten the risk of contracting or spreading STDs.
6) Dating Apps and Social Media: The use of dating apps and social media can facilitate casual sexual encounters and potentially lead to an increase in sexual partners, impacting STD transmission rates.
7) Antibiotic Resistance: Some STDs, like gonorrhea, have developed antibiotic resistance, making them harder to treat.
8) Healthcare Access: Limited access to healthcare services, including STD testing and treatment, can result in undiagnosed and untreated infections.
9) Global Travel and Migration: Increased global travel and migration can introduce new strains of STDs into communities and contribute to their spread.
10) Inadequate Funding for STD Programs: Funding for public health programs related to STD prevention and education has been inconsistent, which can limit their effectiveness.
11) Screening and Reporting Practices: Differences in screening and reporting practices among healthcare providers and health departments can affect the accuracy of data on STD rates.
12) Aging Population: An increasing number of older adults engaging in sexual activity may contribute to higher STD rates if safe sexual practices and testing are not followed.
It's important to note that addressing the rise of STDs requires a multifaceted approach, including comprehensive sexual education, promoting safe sexual practices, reducing stigma, improving access to healthcare, and developing public health programs that target at-risk populations. Regular testing, early diagnosis, and prompt treatment are essential in controlling the spread of STDs and reducing their impact on public health. Public health agencies and organizations continue to work on strategies to combat the rising rates of STDs in the United States.
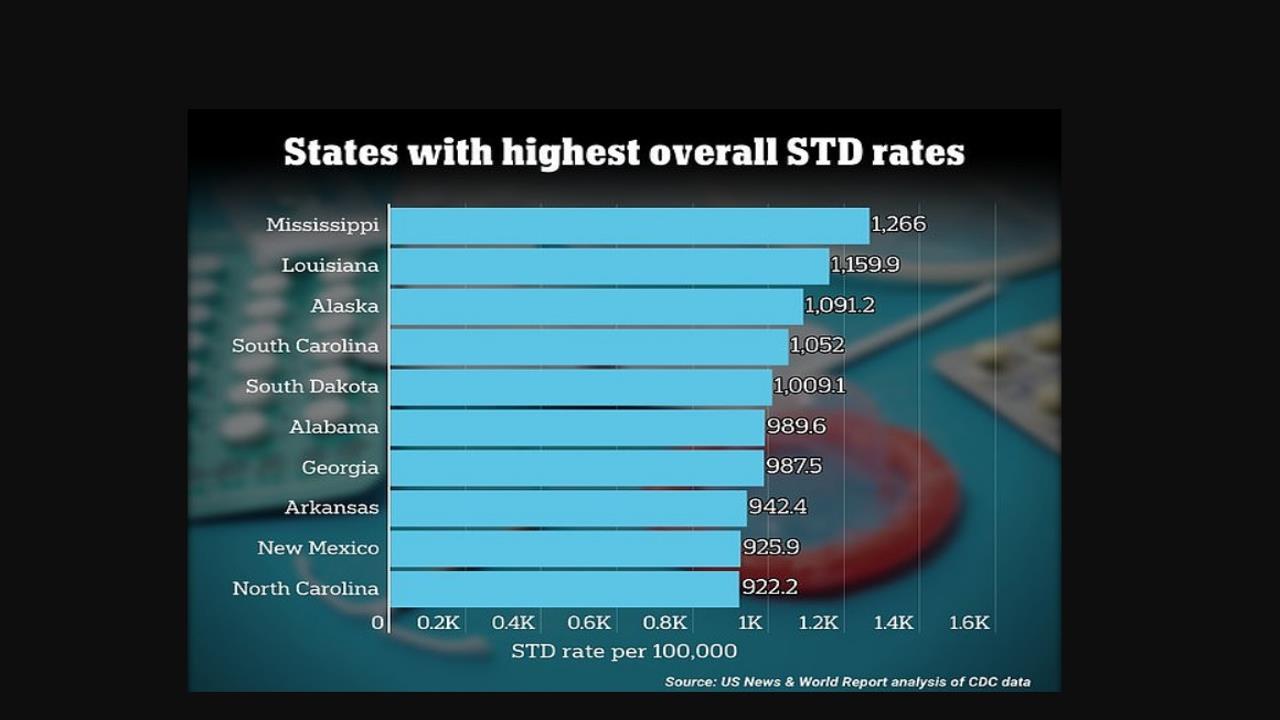
Chart:
References:


Comments