Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Several factors can contribute to high house prices despite decreasing housing affordability:
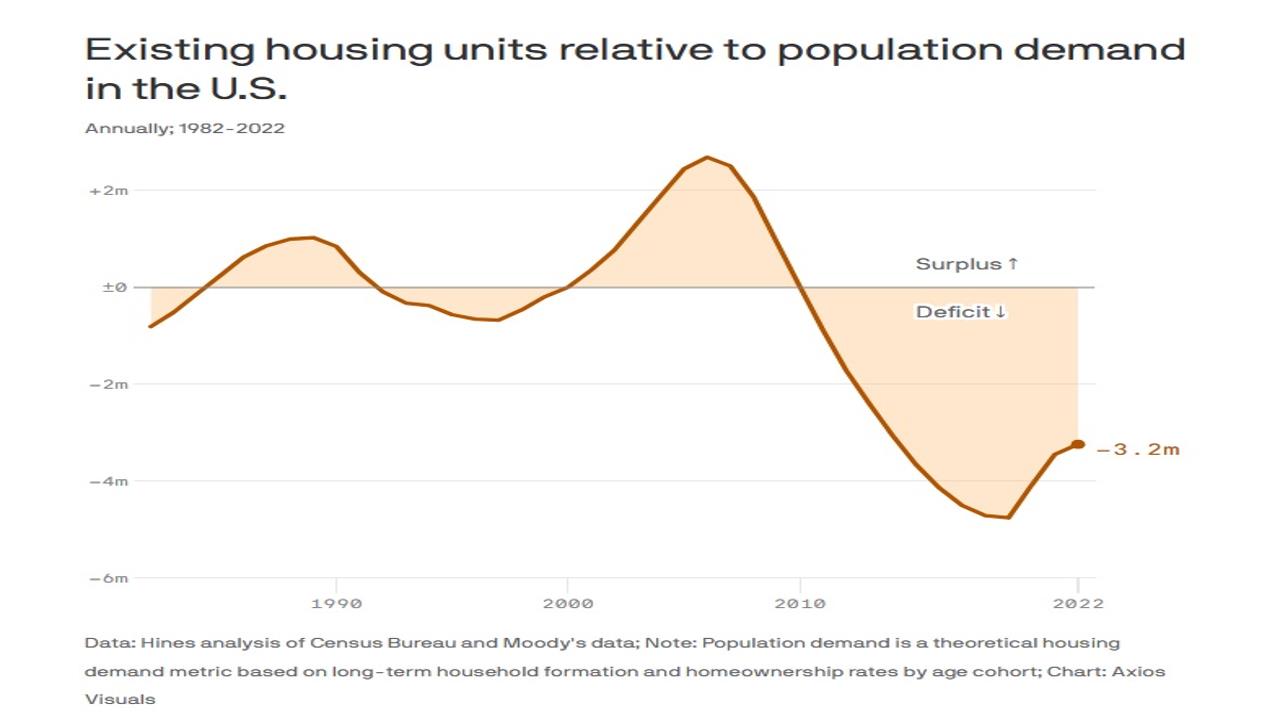
1) Supply and Demand Imbalance: In many regions, there's a persistent shortage of housing relative to the demand. Rapid population growth, limited land availability for construction, zoning restrictions, and lengthy approval processes for new developments can all constrain housing supply. When demand outstrips supply, prices tend to rise.
2) Low Interest Rates: Historically low interest rates can stimulate demand for housing as borrowing becomes more affordable. This increased demand can push prices higher, even if it reduces affordability for many buyers.
3) Speculation and Investment: Real estate can be seen as an attractive investment, leading to speculation in housing markets. Investors purchasing properties for rental income or capital appreciation can drive up prices, particularly in desirable areas.
4) Urbanization and Location Preference: Urban areas with strong economies and amenities often command higher housing prices due to higher demand. Limited availability of affordable housing in these locations can contribute to higher overall prices.
5) Income Disparities: Growing income inequality can result in a situation where certain segments of the population, particularly those with higher incomes, can afford housing even as it becomes less affordable for others.
6) Government Policies and Regulations: Policies such as tax incentives for homeownership, mortgage assistance programs, or zoning regulations that limit new construction can impact housing prices.
7) Market Psychology: Expectations of future price appreciation can influence current buying behavior. If people believe that housing prices will continue to rise, they may be willing to pay higher prices now to avoid even higher costs in the future.
The combination of these factors can create a scenario where housing prices remain high, outpacing the affordability levels for many potential buyers. This situation can lead to housing affordability challenges for a significant portion of the population, especially in regions with strong economic growth and limited housing supply.
Chart:
References:


Comments