Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Corporate profits are influenced by a variety of macroeconomic factors. Understanding these drivers helps to analyze the overall health and performance of businesses within an economy. Some of the main macroeconomic drivers of increased corporate profits include:
1) Economic Growth: Corporate profits are often positively correlated with overall economic growth. When the economy is expanding, businesses tend to experience increased demand for goods and services, leading to higher sales and profits.
2) Consumer Spending: Consumer spending is a major driver of corporate profits, especially in industries related to retail, consumer goods, and services. When consumers have confidence in the economy and their financial situation, they are more likely to spend, contributing to higher corporate revenues.
3) Investment Levels: Business investment, including spending on capital goods and expansion projects, can drive increased productivity and profitability. When businesses invest in new technologies or expand their operations, it can positively impact their bottom line.
4) Interest Rates: The cost of borrowing, influenced by interest rates set by central banks, can impact corporate profits. Lower interest rates generally lead to reduced borrowing costs for businesses, potentially boosting their profitability.
5) Inflation: While moderate inflation is generally considered normal, hyperinflation can erode corporate profits by increasing costs. On the other hand, companies with pricing power may be able to pass on increased costs to consumers.
6) Currency Exchange Rates: Companies that operate internationally may be affected by fluctuations in currency exchange rates. A weaker domestic currency can benefit exporters by making their goods more competitive on the global market, potentially increasing profits.
7) Labor Market Conditions: Wage levels and employment rates can impact corporate profits. In times of low unemployment and high demand for skilled labor, businesses may face higher wage costs, affecting their profitability.
8) Government Policies: Fiscal and monetary policies implemented by governments can influence corporate profits. Tax policies, subsidies, and regulatory changes can either support or hinder business activities.
9) Global Economic Conditions: The interconnectedness of the global economy means that corporate profits can be influenced by economic conditions in major trading partners. Changes in international demand and supply chains can impact the performance of multinational corporations.
10) Technological Advances: Advances in technology can enhance efficiency and reduce production costs for businesses. Companies that embrace technological innovations may experience increased profitability.
11) Commodity Prices: Industries that rely on commodities as inputs may be sensitive to changes in commodity prices. For example, lower commodity prices can benefit companies in sectors like manufacturing and transportation.
It's important to note that these factors interact in complex ways, and their impact on corporate profits can vary across industries and regions. Additionally, the business cycle, financial market conditions, and other external shocks can also influence corporate profitability.
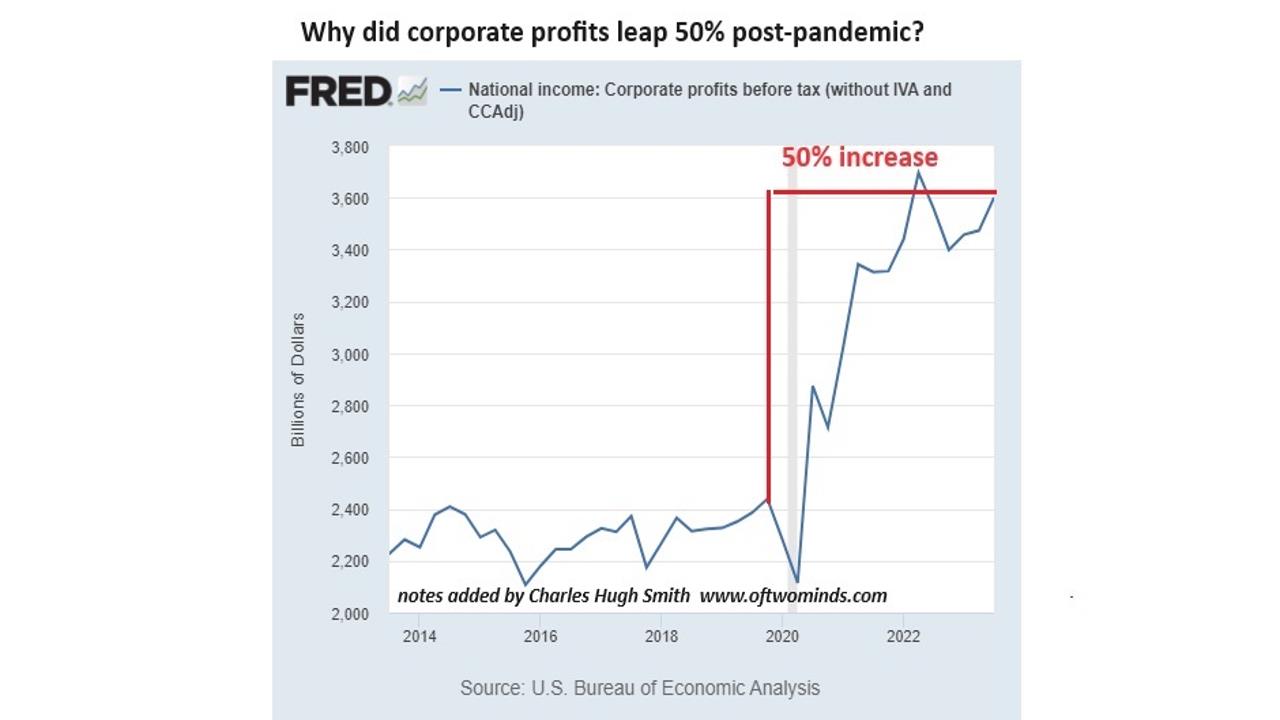
Chart:
References:


Comments