Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
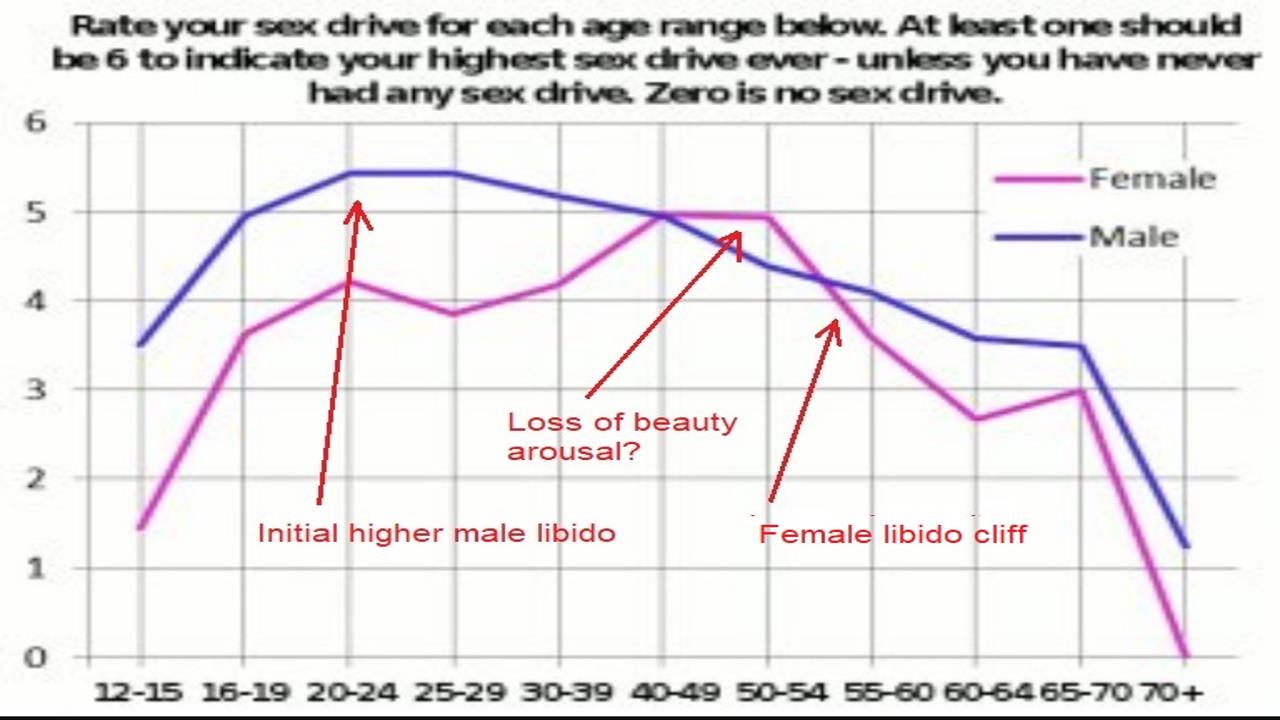
The libido, or sexual desire, can vary between individuals and is influenced by a combination of biological, psychological, and social factors. It's important to note that there is considerable diversity within each gender, and generalizations might not capture individual experiences accurately. However, some broad trends can be observed in the differences between male and female libido over the course of their lifetimes.
Male Libido:
Puberty and Adolescence (Teens to Early 20s): Males typically experience an increase in libido during puberty due to hormonal changes, particularly the surge in testosterone. Sexual curiosity and exploration are common during this period.
Young Adulthood (20s to 30s): Libido tends to remain relatively high during young adulthood. Testosterone levels are generally at their peak, contributing to a sustained interest in sexual activity.
Middle Adulthood (30s to 50s): While testosterone levels may gradually decline with age, many men maintain a consistent libido. Factors such as overall health, stress, and relationship dynamics become increasingly influential during this phase.
Late Adulthood (50s and Beyond): Libido may decline with age for some men, influenced by both physical and psychological factors. However, individual experiences vary widely, and some men maintain a healthy libido well into their later years.
Female Libido:
Puberty and Adolescence (Teens to Early 20s): Similar to males, females may experience an increase in libido during puberty. Hormonal changes, including the rise in estrogen and progesterone, contribute to the development of sexual interest.
Young Adulthood (20s to 30s): Libido is generally stable during this period, with fluctuations influenced by factors such as hormonal changes, stress, and relationship dynamics. For many women, sexual desire may peak in their late 20s or early 30s.
Middle Adulthood (30s to 50s): Hormonal changes, especially during the menstrual cycle and menopause, can impact libido. Relationship satisfaction, psychological well-being, and overall health play crucial roles in maintaining sexual desire during these years.
Late Adulthood (50s and Beyond): Menopause, typically occurring in the late 40s or early 50s, can bring about changes in hormonal levels, leading to a decline in libido for some women. However, individual experiences vary, and many women continue to enjoy a satisfying sexual life well into their later years.
It's essential to emphasize that these are general trends, and individual experiences can deviate significantly. Additionally, psychological and emotional factors, along with cultural and societal influences, play crucial roles in shaping the libido of both men and women across their lifetimes. Open communication and a holistic approach to sexual health are important for addressing individual needs and maintaining a fulfilling sexual life.
Chart:
References:


Comments