Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
A long, protracted war can have various economic effects on a country's GDP, and these effects are generally negative. Here are some ways in which a prolonged conflict can impact the economy:
Direct Costs of Warfare: The financial burden of financing a war, including expenses for military operations, equipment, personnel, and reconstruction, can strain a country's budget. Increased government spending on the military can lead to budget deficits.
Resource Allocation: Resources that could be used for productive economic activities, such as infrastructure development, healthcare, and education, are redirected towards military efforts, leading to a diversion of resources away from civilian needs.
Destruction of Infrastructure: Wars often result in the destruction of infrastructure, including roads, bridges, factories, and homes. The cost of rebuilding and repairing this infrastructure contributes to economic strain.
Displacement of Population: Large-scale displacement of people due to conflict can disrupt labor markets, decrease productivity, and strain social services, negatively impacting the overall economic structure.
Human Capital Loss: Loss of life and injuries among the working-age population can lead to a decrease in human capital, affecting the labor force and reducing productivity.
Uncertainty and Reduced Investment: Prolonged conflict creates an atmosphere of uncertainty, deterring domestic and foreign investment. Businesses may delay or scale back investments due to instability and insecurity.
Trade Disruptions: Wars can disrupt international trade routes and relationships, affecting a country's ability to export and import goods. Trade disruptions can have long-term consequences for economic growth.
Increased Debt: Countries involved in prolonged conflicts often resort to borrowing to finance war-related expenses. This can result in a significant increase in national debt, with long-term economic consequences.
Inflation and Currency Depreciation: War-related spending, coupled with economic disruptions, can contribute to inflation and currency depreciation, eroding the purchasing power of the population.
Social and Political Instability: The economic consequences of war are often intertwined with social and political instability. Economic hardships can contribute to social unrest and political challenges, further complicating the recovery process.
It's important to note that the specific impact of war on GDP can vary based on factors such as the scale of the conflict, the country's economic structure, and the effectiveness of post-war reconstruction efforts. Countries that experience prolonged conflict often face significant challenges in rebuilding their economies and restoring stability.
Chart:
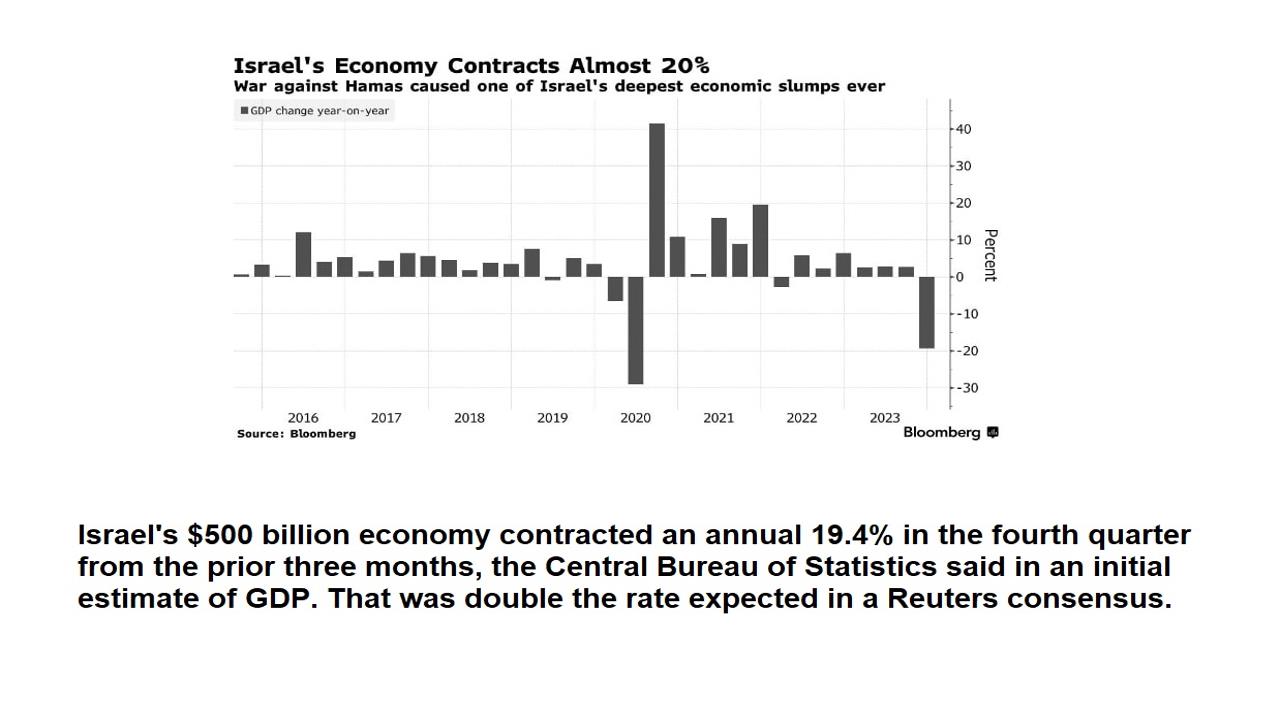
References:


Comments