Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Comparing the carbon footprints of humans, cows, cars, and dogs involves considering various factors, including direct and indirect emissions associated with each. The approximate figures for the carbon footprints of humans, cows, cars, and dogs. Keep in mind that these values can vary based on specific circumstances, methodologies used in calculations, and regional variations:
Humans: The global average carbon footprint for an individual is around 4-6 metric tons of CO2 equivalent per year.
Cows: The carbon footprint of beef production is estimated to range from 15 to 30 kilograms of CO2 equivalent per kilogram of beef produced, depending on various factors such as farming practices and location.
Cars: The carbon footprint of a traditional gasoline or diesel car can vary widely based on fuel efficiency and distance traveled. As a rough estimate, an average gasoline car might emit around 2-3 kg of CO2 per liter of fuel burned. Electric cars, when charged with electricity from a mix of sources, can have a carbon footprint of 50-150 grams of CO2 per kilometer traveled.
Dogs: The carbon footprint of a medium-sized dog is estimated to be around 0.9 metric tons of CO2 equivalent per year. This is roughly equivalent to driving a car for about 2,500 miles (4,000 kilometers).
It's important to note that these figures are general estimates, and actual values can vary based on specific contexts, lifestyle choices, and other factors. Additionally, ongoing efforts in sustainable practices, such as adopting renewable energy sources, reducing meat consumption, and choosing eco-friendly transportation options, can contribute to lowering individual and collective carbon footprints.
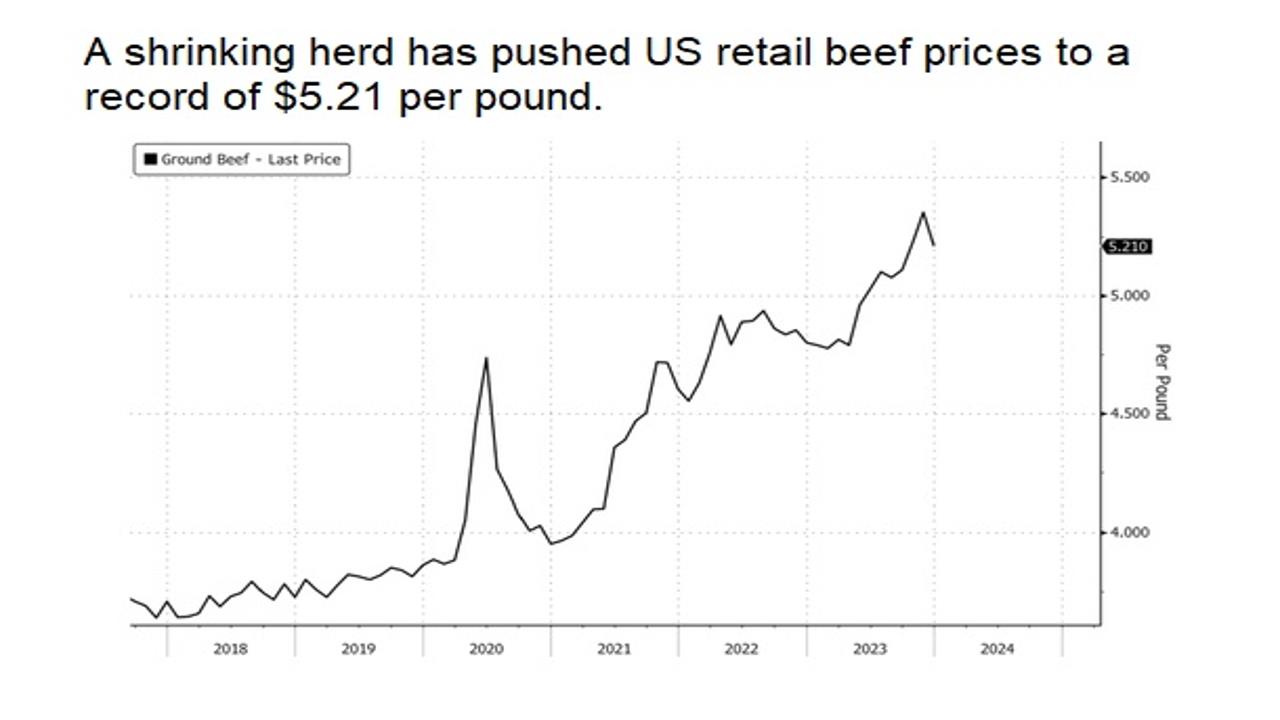
Chart:
References:


Comments