Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Several factors can contribute to longer wait times in emergency room (ER) care:
Patient Volume: High patient volumes, especially during peak hours or seasons, can overwhelm ER staff and lead to longer wait times. A sudden influx of patients due to accidents, natural disasters, or outbreaks can also strain resources and increase wait times.
Severity of Cases: Patients with severe or life-threatening conditions typically receive priority in the ER. If there are multiple critical cases requiring immediate attention, patients with less urgent needs may experience longer wait times.
Staffing Levels: Inadequate staffing, either due to staffing shortages, turnover, or unexpected absences, can slow down the delivery of care in the ER. A lack of available healthcare providers, including physicians, nurses, and support staff, can contribute to delays in assessment, treatment, and discharge.
Resource Availability: Limited availability of diagnostic tests, imaging facilities, treatment rooms, and specialized medical equipment can lead to bottlenecks in the ER. Delays in obtaining test results or accessing necessary resources can prolong wait times for patients.
Complexity of Cases: Patients with complex medical conditions or multiple health issues may require more time and resources to evaluate and treat. These cases can tie up staff and resources, leading to longer wait times for other patients.
Admission and Discharge Processes: Delays in admitting patients to the hospital or arranging transfers to other facilities can contribute to overcrowding in the ER. Similarly, delays in arranging follow-up care, prescriptions, or transportation for discharged patients can prolong their stay in the ER.
Systemic Issues: Systemic issues within the healthcare system, such as inefficiencies in patient flow, communication breakdowns between healthcare providers, and inadequate coordination of care, can exacerbate wait times in the ER.
Addressing these factors requires a multi-faceted approach, including improving resource allocation, optimizing staffing levels, streamlining processes, enhancing communication and coordination among healthcare providers, and implementing strategies to manage patient volume more effectively.
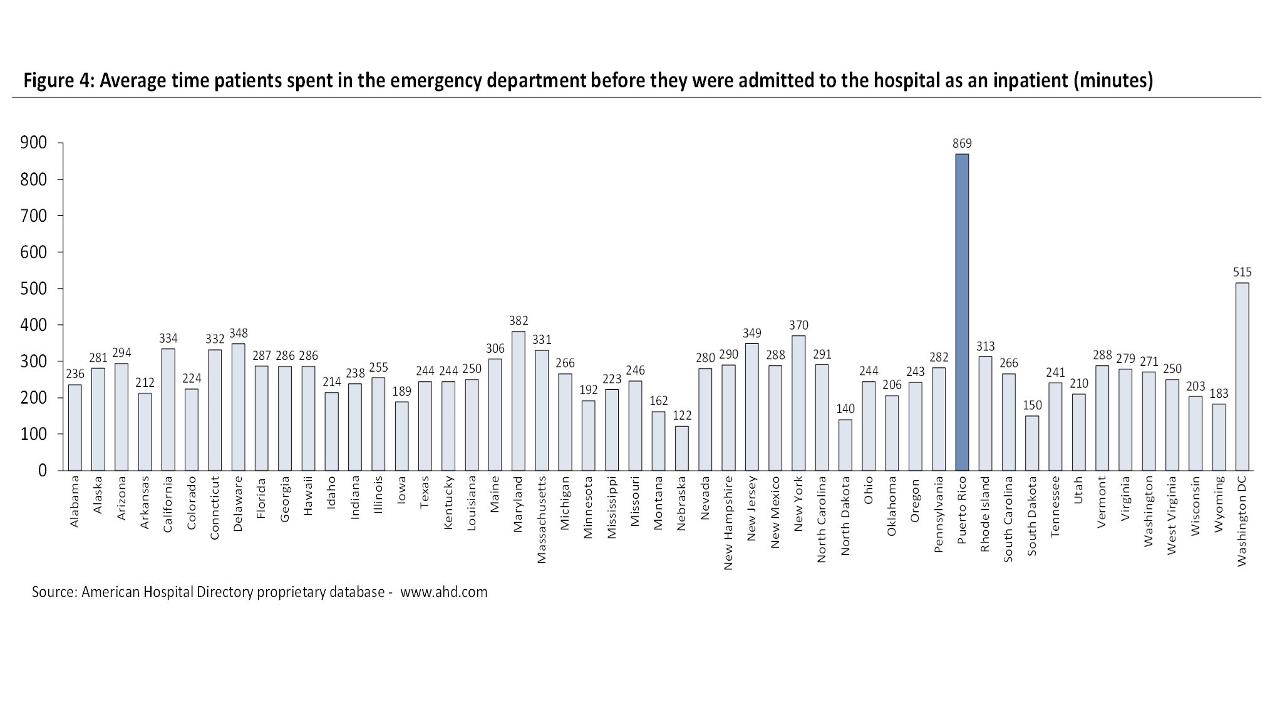
Chart:
References:


Comments