Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Stimulating a stagnant economy requires a combination of fiscal, monetary, and structural policy measures to boost economic activity, create jobs, and restore confidence among businesses and consumers. Here are several strategies that can be employed to stimulate a stagnant economy:
1) Monetary Policy:
Lower Interest Rates: Central banks can lower interest rates to make borrowing cheaper for businesses and consumers. This can encourage spending, investment, and borrowing, leading to increased economic activity.
Quantitative Easing: Central banks can implement quantitative easing programs to inject money into the economy by purchasing financial assets. This can help lower long-term interest rates and support lending.
2) Fiscal Policy:
Government Spending: Increase government spending on infrastructure projects, education, healthcare, and other sectors that create jobs and boost economic activity. This spending can stimulate demand and encourage private sector investment.
Tax Cuts: Reduce taxes for individuals and businesses to increase disposable income and stimulate consumer spending and business investment.
Direct Aid: Provide targeted financial assistance to individuals and businesses affected by economic downturns, such as unemployment benefits and grants for small businesses.
3) Financial Sector Support:
Bank Recapitalization: Ensure that the banking system is stable and well-capitalized to promote lending to businesses and consumers.
Credit Guarantees: Implement credit guarantee programs to encourage banks to extend loans to businesses and individuals, particularly during times of economic stress.
4) Labor Market Reforms:
Labor Market Flexibility: Implement policies that make it easier for businesses to hire and fire workers, which can encourage job creation and reduce unemployment.
Skills Training: Invest in education and skills training programs to improve the employability of the workforce.
5) Structural Reforms:
Deregulation: Reduce bureaucratic hurdles and regulations that may stifle business growth and investment. Trade Policies: Promote trade liberalization to expand export opportunities for businesses, leading to increased economic activity. Innovation and Technology: Encourage innovation and the adoption of new technologies to enhance productivity and competitiveness.
Consumer and Business Confidence: Restore confidence in the economy through clear and transparent policies and communication. Confidence plays a crucial role in consumer spending and business investment decisions.
6) Infrastructure Investment: Invest in critical infrastructure projects such as transportation, energy, and communication networks, which can have long-term positive effects on the economy.
7) Sustainable Development: Consider sustainable and environmentally friendly policies and investments that can stimulate economic growth while addressing environmental challenges.
8) Global Cooperation: In some cases, coordination with other countries or international organizations may be necessary to address global economic challenges.
It's important to note that the specific measures needed to stimulate a stagnant economy may vary depending on the unique circumstances and challenges facing that economy. Policymakers often employ a combination of these strategies and continually assess their effectiveness to adapt as needed. Additionally, the success of these measures depends on the collaboration and support of various stakeholders, including government, businesses, and consumers.
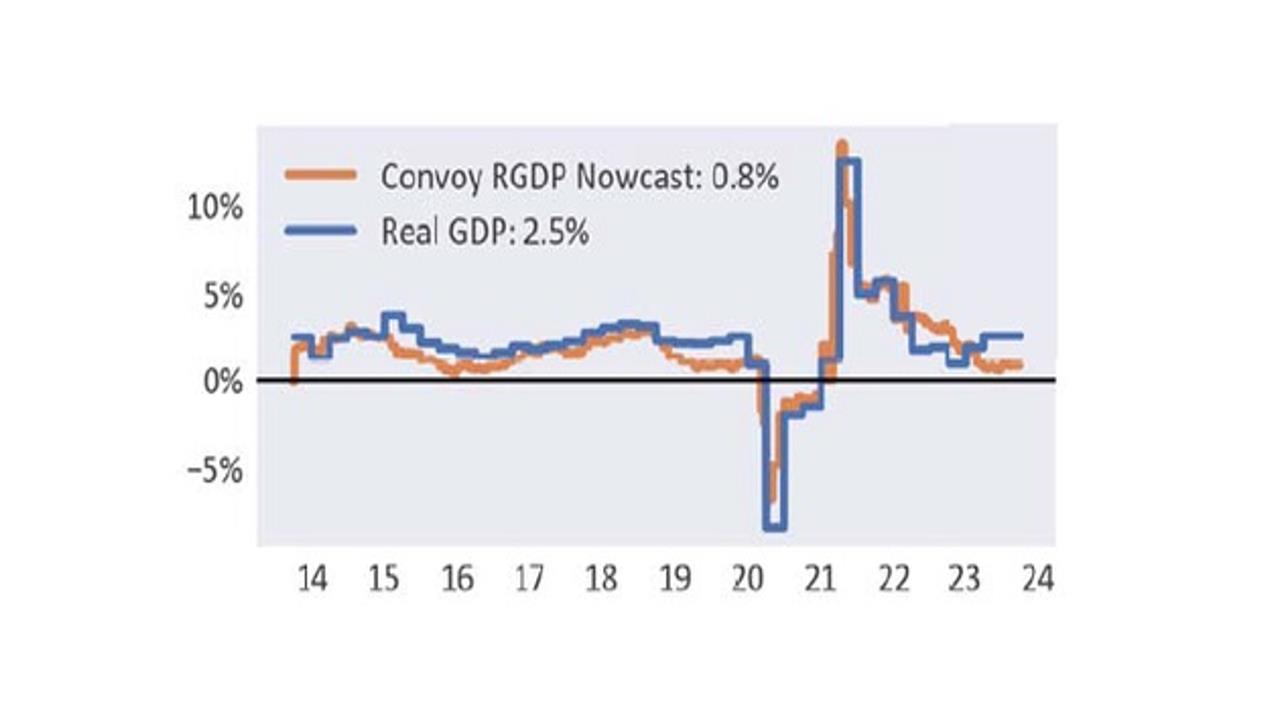
Chart:
References:

Comments