Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Bee populations in the United States and around the world have been experiencing declines in recent years, and there are several factors contributing to this trend:
1) Pesticides: The use of neonicotinoid pesticides has been linked to bee population declines. These pesticides are used in agriculture to protect crops from insect pests, but they can also harm non-target insects, including bees. Pesticide exposure weakens bees, making them more susceptible to diseases and reducing their ability to forage for food.
2) Habitat Loss: Urbanization and agricultural expansion have led to the loss of natural habitats for bees. Bees need a variety of flowering plants for nectar and pollen, and the destruction of these habitats limits their access to essential food sources.
3) Monoculture Agriculture: Large-scale monoculture farming practices, where vast areas are planted with a single crop, limit the diversity of available food sources for bees. This can lead to nutritional deficiencies and reduced bee health.
4) Climate Change: Climate change can disrupt the timing and availability of flowers, affecting the seasonal availability of food for bees. Extreme weather events and shifts in temperature can also impact bee populations.
5) Disease and Parasites: Bees can be affected by various diseases and parasites, including the Varroa destructor mite, which weakens bee colonies by feeding on bee larvae and transmitting diseases. These health challenges can significantly reduce bee populations.
6) Stress from Commercial Beekeeping: Commercial beekeeping involves the transportation of bee colonies long distances to pollinate various crops. This can stress bees and make them more susceptible to diseases and environmental factors.
7) Lack of Genetic Diversity: Commercial bee breeding often prioritizes certain traits, such as high honey production or disease resistance, over genetic diversity. This can make bee populations more vulnerable to environmental changes and diseases.
Efforts are being made to address these issues and promote bee conservation. These efforts include the banning or restricting of certain pesticides, the creation of pollinator-friendly habitats, and research into breeding more resilient bee populations. Bees play a crucial role in pollinating many of the crops we rely on for food, so their decline is a matter of concern for agriculture and ecosystems alike.
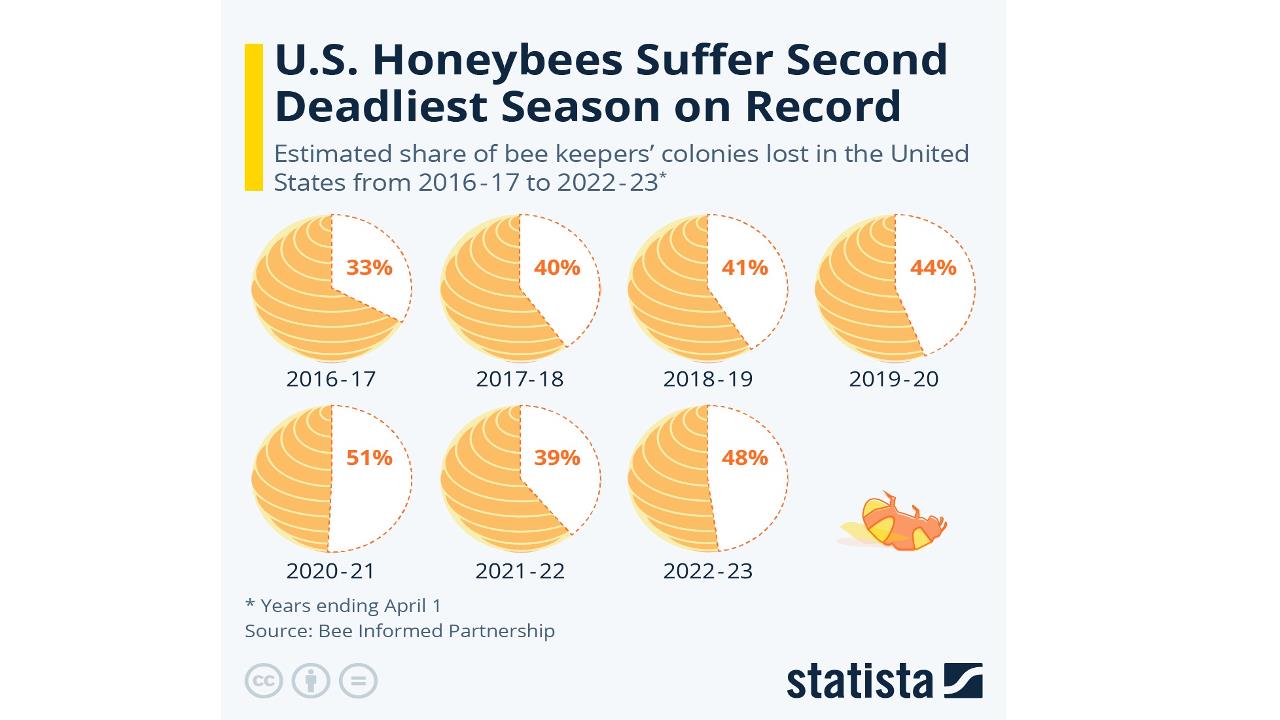
Chart:
References:


Comments