Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Closing the advantage gap between homeowners and renters in the event of inflation can be a complex challenge, as homeownership and renting come with different financial dynamics. Inflation can affect both homeowners and renters, but it may impact them differently. To address this gap, governments can consider several policy options:
1) Rent Control or Rent Stabilization: Implement or strengthen rent control or rent stabilization policies to limit how much landlords can increase rents. This can provide stability for renters, especially during periods of high inflation.
2) Affordable Housing Programs: Invest in affordable housing programs to increase the supply of affordable rental units. This can help mitigate the impact of rising rents during inflationary periods.
3) Subsidized Housing: Expand subsidized housing programs for low-income individuals and families to ensure they have access to affordable housing options.
4) Tenant Protections: Strengthen tenant protections, such as eviction moratoriums and regulations against unfair eviction practices, to provide renters with more security in their housing situations.
5) Property Tax Relief: Consider property tax relief programs for homeowners to help alleviate the financial burden of rising property taxes during inflation.
6) Incentives for Landlords: Provide incentives for landlords to keep rents stable during inflation, such as tax breaks or incentives to invest in property improvements without raising rents significantly.
7) Housing Vouchers: Increase funding for housing voucher programs to assist low-income renters in paying for housing. These vouchers can help bridge the gap between rental costs and a tenant's income.
8) Financial Literacy and Education: Offer financial literacy programs and education to renters to help them manage their finances effectively during periods of inflation.
9) Homeownership Assistance: Develop programs to promote homeownership among renters who aspire to buy homes. This may include down payment assistance, favorable mortgage terms, or housing counseling.
10) Community Land Trusts: Support and expand community land trust initiatives, which can provide affordable housing options and protect against gentrification in certain areas.
11) Infrastructure and Transportation: Invest in public transportation and infrastructure development to create more affordable housing options in well-connected areas, reducing the advantage of homeownership in desirable locations.
12) Inflation-Indexed Rent Increases: Consider allowing rent increases that are indexed to inflation, which can provide a fair balance between the interests of landlords and renters.
13) Rental Assistance Programs: Expand or create rental assistance programs to provide direct financial assistance to renters facing rent increases due to inflation.
14) Community Development: Promote community development efforts that prioritize affordable housing construction and maintenance, fostering stable neighborhoods.
15) Data and Monitoring: Collect and analyze data on housing costs, inflation rates, and rental market trends to inform policy decisions and adjustments.
It's important to recognize that addressing the advantage gap between homeowners and renters during inflation may require a combination of these strategies, as the effectiveness of each approach can vary based on local economic conditions and housing market dynamics. Additionally, policymakers should consider the potential unintended consequences of certain policies and aim to strike a balance between protecting renters and ensuring a healthy housing market.
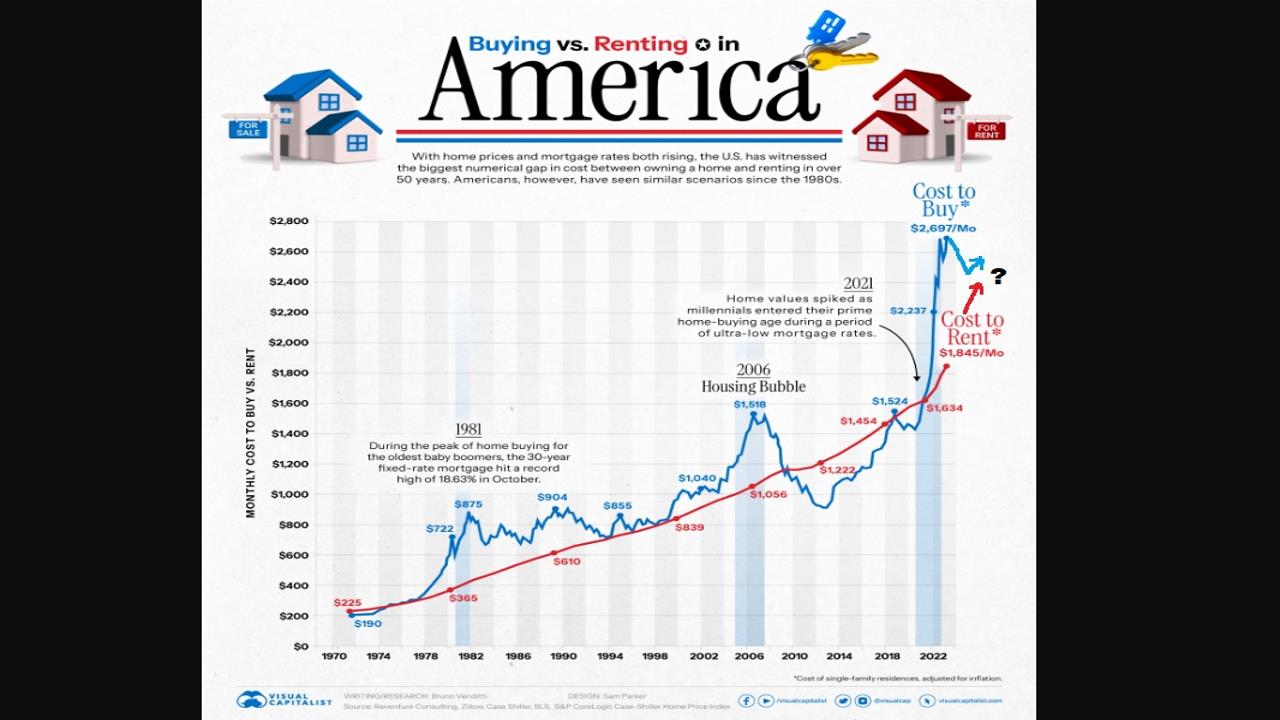
Chart:
References:


Comments