Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
The dissatisfaction of younger workers in the workforce can be influenced by a combination of factors, many of which have evolved over time. While it's important to note that not all younger workers are dissatisfied, here are some common reasons for dissatisfaction among this demographic:
Economic Factors:
1) Wage Stagnation: Many younger workers are experiencing wage stagnation, where their incomes are not increasing at the same rate as the cost of living. This can make it difficult to achieve financial stability and meet basic needs.
2) Student Loan Debt: A significant portion of younger workers may be burdened with student loan debt, limiting their financial flexibility and causing stress.
Job Insecurity:
1) Gig Economy: The rise of the gig economy and temporary or contract work has led to increased job insecurity for many younger workers, who may struggle to find stable, long-term employment.
2)Automation: Automation and advances in technology have led to concerns about job displacement and the need for constant upskilling.
Work-Life Balance:
1) Demanding Work Hours: Some younger workers may face demanding work hours and have difficulty balancing work with personal life, leading to burnout and dissatisfaction.
2) Remote Work Challenges: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated remote work, which has its own set of challenges, including feelings of isolation and difficulty in separating work from home life.
Company Culture:
1) Lack of Engagement: Younger workers often seek meaning and purpose in their work, and they may be dissatisfied if they perceive a lack of alignment between their values and the company's mission.
2) Limited Opportunities for Advancement: A perception of limited career growth opportunities within a company can lead to job dissatisfaction.
Mental Health and Well-being:
1) Increased Stress: The pressures of modern life, including the constant connectivity enabled by technology, can contribute to higher levels of stress and mental health concerns among younger workers.
2) Work-Life Balance: Struggles with work-life balance can negatively impact mental health.
Generational Differences: There can sometimes be generational differences in workplace expectations and values. Younger workers may have different priorities and expectations than older generations, leading to dissatisfaction when these differences are not acknowledged or addressed.
Social and Political Factors:
1) Income Inequality: Younger workers may be more aware of income inequality and social justice issues, leading to dissatisfaction when they perceive unfair treatment or policies in the workplace.
2) Climate Concerns: Younger generations are often more concerned about climate change and environmental sustainability, and they may seek employers that align with their values in this regard.
It's important to note that job satisfaction is a complex and individualized issue, and not all younger workers will experience these challenges in the same way. Moreover, younger workers may also have unique strengths and contributions to offer in the workplace, such as digital fluency and adaptability. Employers are increasingly recognizing the importance of addressing these concerns to attract and retain younger talent and create a more inclusive and fulfilling work environment.
Chart:
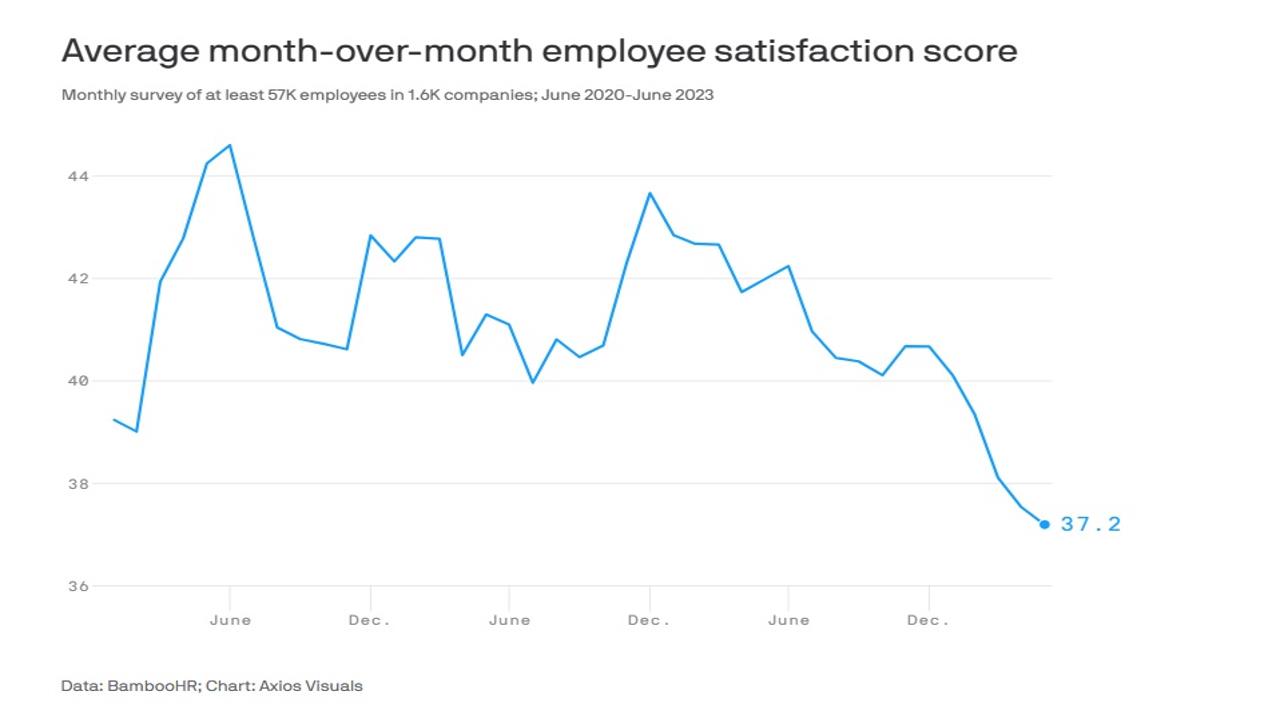
References:


Comments