Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
When the Federal Reserve (Fed) sharply cuts interest rates, it often has several effects on various asset classes:
1) Equities (Stocks): Lower interest rates tend to be favorable for stocks. Cheaper borrowing costs can stimulate economic activity, which can benefit corporate profits and stock prices. Additionally, lower rates make equities relatively more attractive compared to fixed-income investments like bonds, potentially leading investors to move funds into the stock market, driving prices higher.
2) Bonds: Bond prices tend to rise when interest rates fall. As the Fed lowers rates, existing bonds with higher yields become more attractive because they offer higher returns compared to newly issued bonds with lower yields. Therefore, the demand for existing bonds increases, pushing their prices up. Conversely, yields on new bonds issued after the rate cut would generally be lower.
3) Commodities: The impact on commodities can be mixed. Lower interest rates might weaken the value of the currency, making commodities priced in that currency more attractive to international buyers. Also, lower rates can signal expectations of increased economic activity, potentially boosting demand for commodities. However, the effect can vary based on factors like supply and demand dynamics specific to each commodity.
It's important to note that while these are common reactions, market dynamics are complex and affected by various factors, including market sentiment, economic conditions, geopolitical events, and investor expectations. Sharp interest rate cuts by the Fed might have immediate impacts, but the longer-term effects can be influenced by a multitude of factors beyond just the rate decision itself.
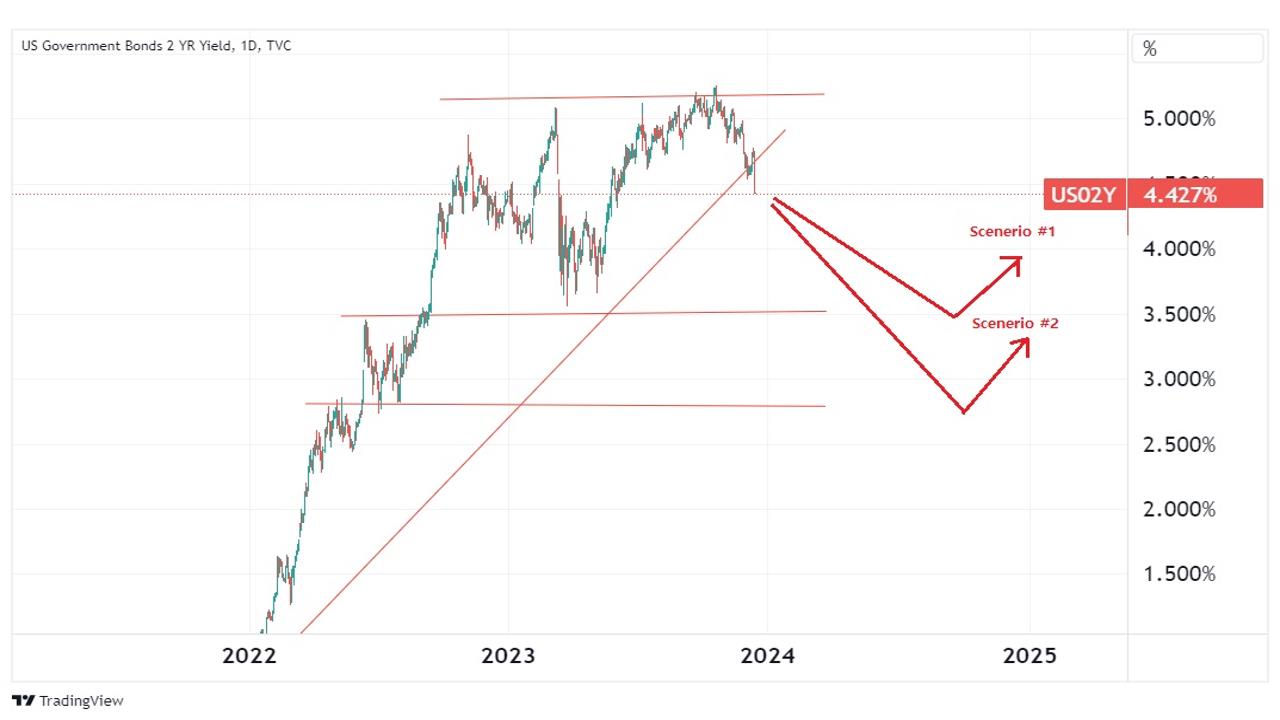
Chart:
References:


Comments