Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Productivity measurement in an economy is important for several reasons:
Economic Growth: Productivity is a key driver of long-term economic growth. Higher productivity means that more output is generated with the same amount of input, leading to increased production capacity and higher living standards over time.
Competitiveness: Productivity improvements can enhance the competitiveness of businesses and industries in the global marketplace. More efficient production processes allow firms to lower costs, improve quality, and offer competitive prices, enabling them to capture market share and expand exports.
Resource Allocation: Productivity measurement helps policymakers and businesses allocate resources more efficiently. By identifying sectors or activities with low productivity, policymakers can target investments, incentives, and reforms to spur innovation, enhance skills, and modernize infrastructure, thereby boosting overall productivity growth.
Wage Growth: Rising productivity can lead to higher wages and improved living standards for workers. When workers become more productive, they can command higher wages without causing inflationary pressures, as increased output offsets higher labor costs.
Government Revenues: Higher productivity can contribute to increased tax revenues for governments. As incomes rise due to productivity gains, individuals and businesses pay more in taxes, providing governments with additional resources to fund public services and investments.
Several factors drive good or bad productivity measurements:
Technology and Innovation: Technological advancements and innovation play a crucial role in driving productivity growth. Investments in research and development, adoption of new technologies, and improvements in production processes can lead to significant productivity gains.
Human Capital: The skills, knowledge, and education level of the workforce are important determinants of productivity. Investments in education, training, and lifelong learning can enhance human capital and contribute to higher productivity levels.
Infrastructure: Adequate infrastructure, including transportation networks, communication systems, and utilities, is essential for facilitating efficient production and distribution of goods and services. Poor infrastructure can impede productivity growth by increasing transportation costs, reducing connectivity, and causing delays.
Regulatory Environment: Regulatory policies and institutions can affect productivity by either facilitating or hindering business operations. Excessive regulations, bureaucratic inefficiencies, and barriers to entry can stifle innovation, entrepreneurship, and investment, leading to lower productivity levels.
Market Competition: Competitive markets incentivize firms to improve efficiency, innovate, and invest in productivity-enhancing technologies. On the other hand, monopolistic or oligopolistic market structures may reduce incentives for firms to innovate and improve productivity, leading to lower overall productivity levels.
Workplace Practices: Management practices, organizational culture, and employee engagement can influence productivity outcomes. Effective leadership, clear communication, employee empowerment, and performance incentives can foster a culture of productivity and continuous improvement.
Macro-economic Factors: Macroeconomic conditions, such as monetary policy, fiscal policy, exchange rates, and global economic trends, can also impact productivity levels. Stable macroeconomic conditions, conducive to investment and growth, are generally associated with higher productivity.
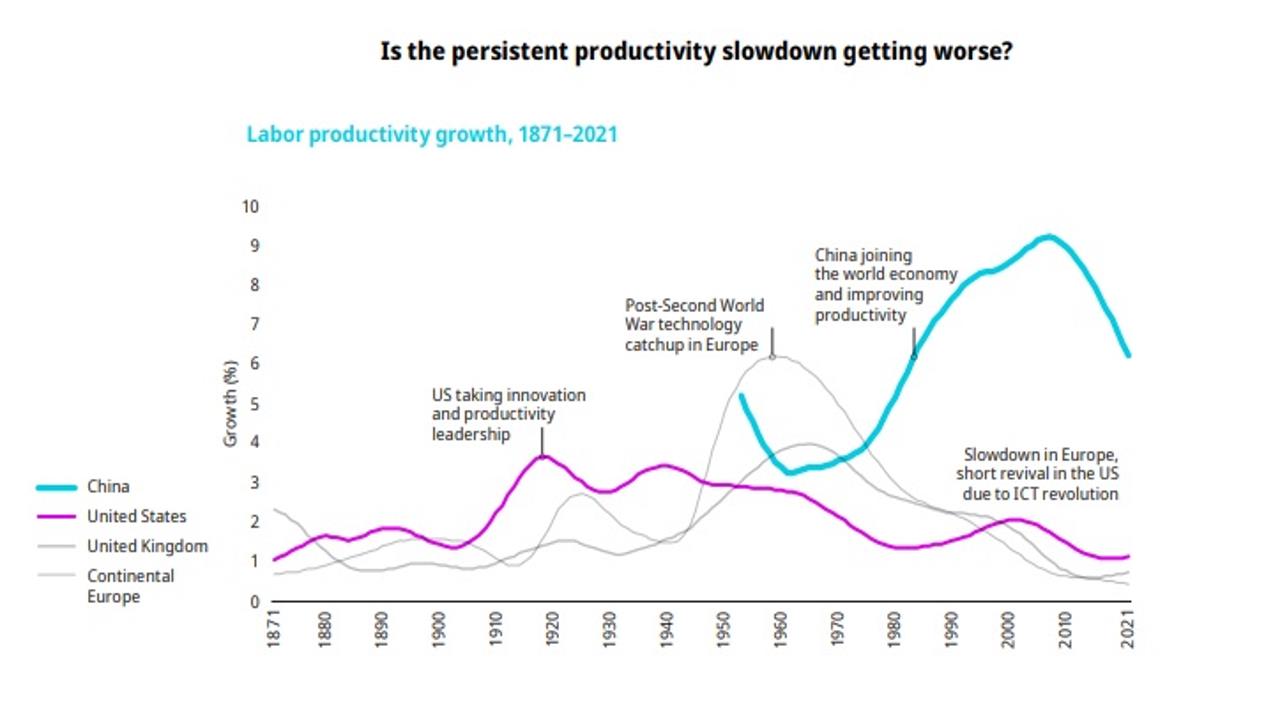
Chart:
References:


Comments