Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Geopolitical biases against Jews and Muslims have distinct historical, cultural, and regional contexts, making direct comparisons challenging. However, there are some similarities and differences in how these biases manifest:
Similarities:
Historical Roots:
Jews: Anti-Semitism has deep historical roots in Europe and the Middle East, stemming from religious, economic, and cultural prejudices. Muslims: Islamophobia has been fueled by historical conflicts like the Crusades, colonialism, and more recently, global terrorism concerns.
Modern Political Climate:
Both Jews and Muslims face biases linked to modern geopolitical conflicts. For Jews, the Israeli-Palestinian conflict often influences perceptions and biases. For Muslims, events like 9/11, the rise of ISIS, and the refugee crisis contribute to Islamophobic sentiments. Stereotyping and Discrimination:
Both groups are subject to stereotyping and discrimination. Jews often face stereotypes about financial control and dual loyalty, while Muslims frequently encounter stereotypes about terrorism and cultural backwardness.
Differences:
Regional Variations:
Anti-Semitism is notably prevalent in Europe and parts of the Middle East, whereas Islamophobia is more widespread in Western countries, especially the United States and Europe.
Cultural and Religious Factors:
Anti-Semitic biases often center around cultural and religious differences, as well as historical scapegoating. Islamophobic biases tend to focus more on perceived threats to security and cultural integration.
Media Representation:
Media portrayal can differ significantly. Jews are often depicted in the context of the Holocaust and the Israeli state, while Muslims are frequently represented in relation to terrorism and extremism.
Legislative and Institutional Responses:
Different countries have varying levels of institutional responses to these biases. For instance, Holocaust denial is a crime in some European countries, while anti-Islamophobia laws and measures are less uniformly implemented.
Impact:
Social and Economic Impact:
Both forms of bias can lead to social exclusion, economic disadvantages, and hate crimes. However, the intensity and nature of these impacts can vary based on the local context and the prevailing political climate.
Community Responses:
Both Jewish and Muslim communities have developed various forms of resistance and advocacy to combat these biases, but the strategies and effectiveness can differ.
In summary, while there are similarities in how Jews and Muslims experience geopolitical biases, the specific historical contexts, cultural factors, and regional dynamics lead to distinct forms of prejudice and discrimination against each group.
Chart:
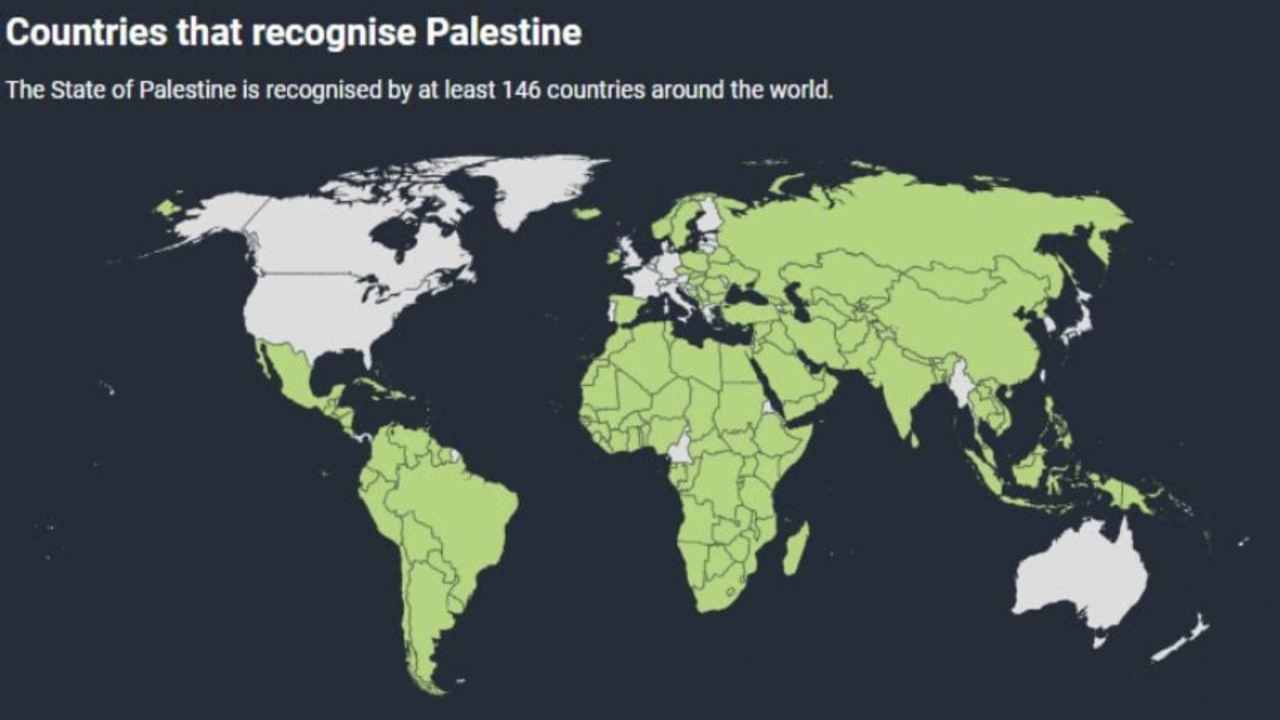
References:


Comments