Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Fascist governments typically exhibit a range of characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of governance. Here are some key attributes:
Authoritarianism: Centralized control by a single leader or a small group, with limited political pluralism and suppression of dissent.
Nationalism: Intense emphasis on national identity, often based on ethnicity, race, or cultural heritage. This often includes a sense of superiority over other nations and peoples.
Militarism: Promotion of military values and readiness for conflict. Fascist regimes often glorify the military and use it to enforce their policies domestically and internationally.
Dictatorship: The presence of a single leader with significant power. This leader often has the ability to make decisions without the need for legislative approval or judicial oversight.
Suppression of Political Opposition: Use of force, propaganda, and legal means to suppress or eliminate political opposition. This includes censorship, imprisonment, or even execution of dissenters.
Control of the Economy: While not always fully state-controlled, fascist economies often have significant government intervention, with an emphasis on autarky (economic self-sufficiency) and the alignment of corporate interests with state goals.
Propaganda and Control of Media: Extensive use of propaganda to maintain the regime’s image and control public opinion. Media is often state-controlled or heavily regulated to prevent dissenting views.
Regulation of Private Life: Intrusion into private life to enforce conformity to state ideology. This includes regulation of education, family life, and sometimes even personal relationships.
Cult of Personality: The leader is often portrayed as a heroic and infallible figure, and the population is encouraged to show unwavering loyalty and devotion.
Anti-democratic Ideology: Rejection of democratic institutions and principles, often accompanied by the belief that democracy is weak and ineffective.
Liberal and conservative governments generally differ in their ideologies, policy priorities, and approaches to governance. Here are some key distinctions:
Liberal: Emphasizes a larger role for government in providing social services, regulating the economy, and ensuring social justice. Advocates for government intervention to address economic and social inequalities. Conservative: Advocates for a smaller government with limited intervention in the economy and individual lives. Emphasizes personal responsibility, free markets, and limited regulation.
Liberal: Supports progressive taxation, social welfare programs, and government spending to stimulate the economy and provide for the needy. Favors regulation to protect consumers, workers, and the environment. Conservative: Favors lower taxes, reduced government spending, and deregulation. Emphasizes free-market principles and believes that private enterprise and competition drive economic growth. Social Policies:
Liberal: Advocates for social progress and equality, supporting issues like LGBTQ+ rights, gender equality, and reproductive rights. Emphasizes the protection of civil liberties and individual freedoms. Conservative: Emphasizes traditional values and often supports policies that align with religious or cultural norms. May oppose abortion, same-sex marriage, and other progressive social changes. Healthcare:
Liberal: Supports universal healthcare and government involvement in ensuring that all citizens have access to medical care. Often advocates for public healthcare systems or significant regulation of private healthcare. Conservative: Prefers private healthcare systems and limited government involvement. Advocates for market-based solutions to healthcare issues, such as health savings accounts and private insurance. Education:
Liberal: Supports public education and increased funding for schools, along with policies to ensure equal access to quality education for all students. Often advocates for government programs to reduce the cost of higher education. Conservative: Advocates for school choice, including charter schools and vouchers for private schooling. Emphasizes parental control over education and often supports policies that reduce federal involvement in education.
Liberal: Prioritizes addressing climate change through regulation, renewable energy investments, and international cooperation. Supports strong environmental protections. Conservative: May prioritize economic growth over environmental regulations. Often skeptical of extensive government intervention in environmental issues and may support traditional energy sources like oil and coal.
Liberal: Generally supports more open immigration policies, a pathway to citizenship for undocumented immigrants, and protections for refugees and asylum seekers. Conservative: Advocates for strict immigration controls, border security, and policies that prioritize national sovereignty and security. Criminal Justice:
Liberal: Emphasizes rehabilitation, criminal justice reform, and addressing systemic inequalities within the justice system. Supports measures to reduce mass incarceration and police reform. Conservative: Focuses on law and order, strong penalties for crime, and support for police and other law enforcement agencies. Often advocates for maintaining or increasing penalties for crimes.
Liberal: Tends to support inclusive decision-making processes that involve various stakeholders, including marginalized groups. Often emphasizes transparency and public participation. Conservative: May prioritize efficiency and decisiveness in decision-making, often favoring more hierarchical or top-down approaches.
Liberal: Supports international cooperation, multilateralism, and engagement in international organizations and agreements. Emphasizes diplomacy and global partnerships. Conservative: May prioritize national sovereignty and unilateral action. Often advocates for a strong national defense and a cautious approach to international commitments and alliances.
Liberal: Generally open to cultural change and diversity, advocating for multiculturalism and the acceptance of different lifestyles and identities. Conservative: Often seeks to preserve traditional cultural norms and values, emphasizing stability and continuity in cultural practices.
These differences can vary in emphasis and implementation based on the specific political context and the particular leaders or parties in power. However, they provide a general framework for understanding the distinctions between liberal and conservative governments.
Chart:
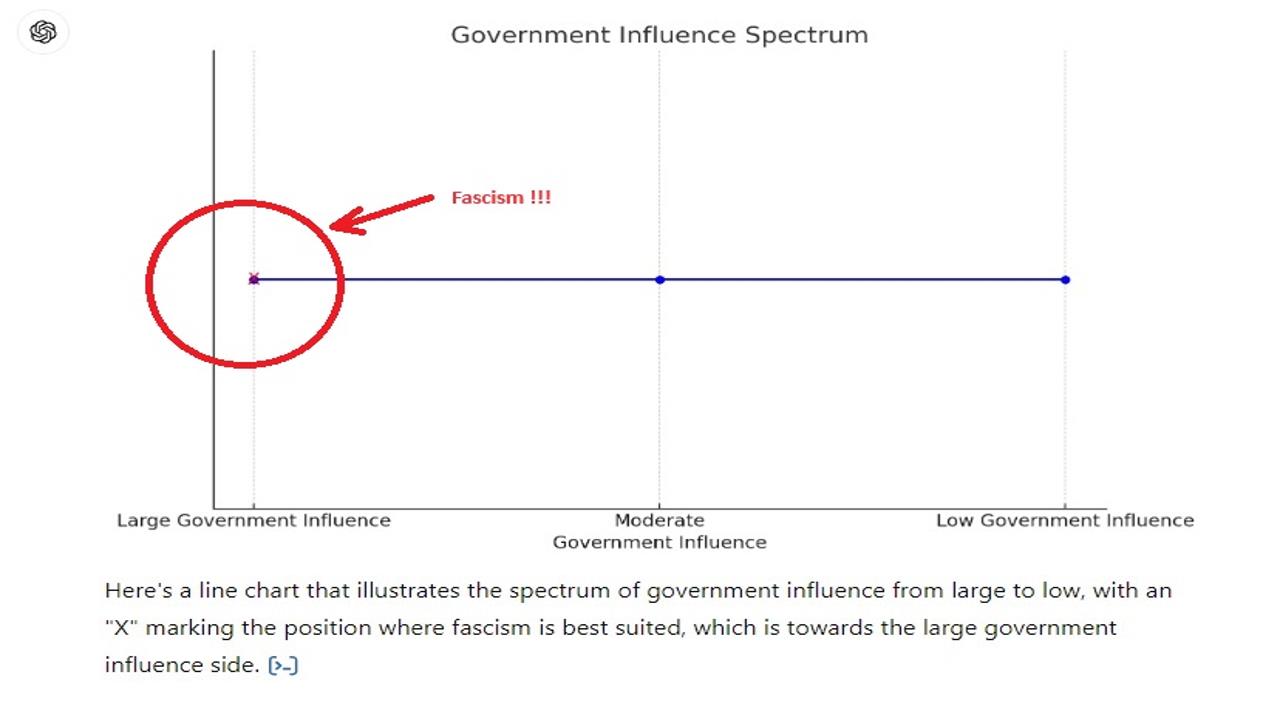
References:


Comments