Video:
Take our online poll:
AI Analysis:
Genocide is a grave international crime and a term that refers to specific acts committed with the intent to destroy, in whole or in part, a national, ethnical, racial, or religious group. It is defined and prohibited under international law, notably in the United Nations Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of the Crime of Genocide, adopted in 1948. Genocide consists of several acts and elements, including:
1) Killing Members of the Group: Genocide involves the act of killing members of a protected group, which can include a national, ethnical, racial, or religious group. This includes not only direct killing but also acts that lead to the deaths of group members, such as through forced labor, starvation, or other means.
2) Causing Serious Bodily or Mental Harm: Genocide includes acts that cause serious bodily or mental harm to members of the targeted group. This can encompass physical violence, torture, sexual violence, and other forms of cruelty.
3) Deliberately Inflicting Conditions Leading to Physical Destruction: This element involves deliberately creating conditions, such as deprivation of basic necessities, which lead to the physical destruction of the group.
4) Imposing Measures to Prevent Births: Genocide can also involve imposing measures intended to prevent births within the targeted group. This can include forced sterilization, forced abortion, or other actions to restrict the ability to have children.
5) Forcibly Transferring Children: Genocide may include forcibly transferring children from the targeted group to another group with the intent of destroying the group's identity. This is often done through forced adoption or assimilation.
6) Intent to Destroy, in Whole or in Part: Perhaps the most crucial element is the specific intent to destroy, in whole or in part, the targeted group. Genocide is not a result of random acts but is driven by a clear and deliberate intention to destroy the group. This intent must be proven to establish genocide.
7) Protected Groups: Genocide applies to specific national, ethnical, racial, or religious groups. These groups are defined by their common characteristics, such as ethnicity, nationality, race, or religion. Genocidal acts can be directed against any of these protected groups.
Genocide is considered one of the most heinous crimes under international law, and individuals who commit or order acts of genocide can be held accountable in national and international courts. The international community, through various mechanisms, has the responsibility to prevent and punish genocide and to protect groups at risk of such violence. Genocide is not limited to mass killings but encompasses a range of acts aimed at the destruction of the targeted group, including cultural and biological forms of destruction.
Chart:
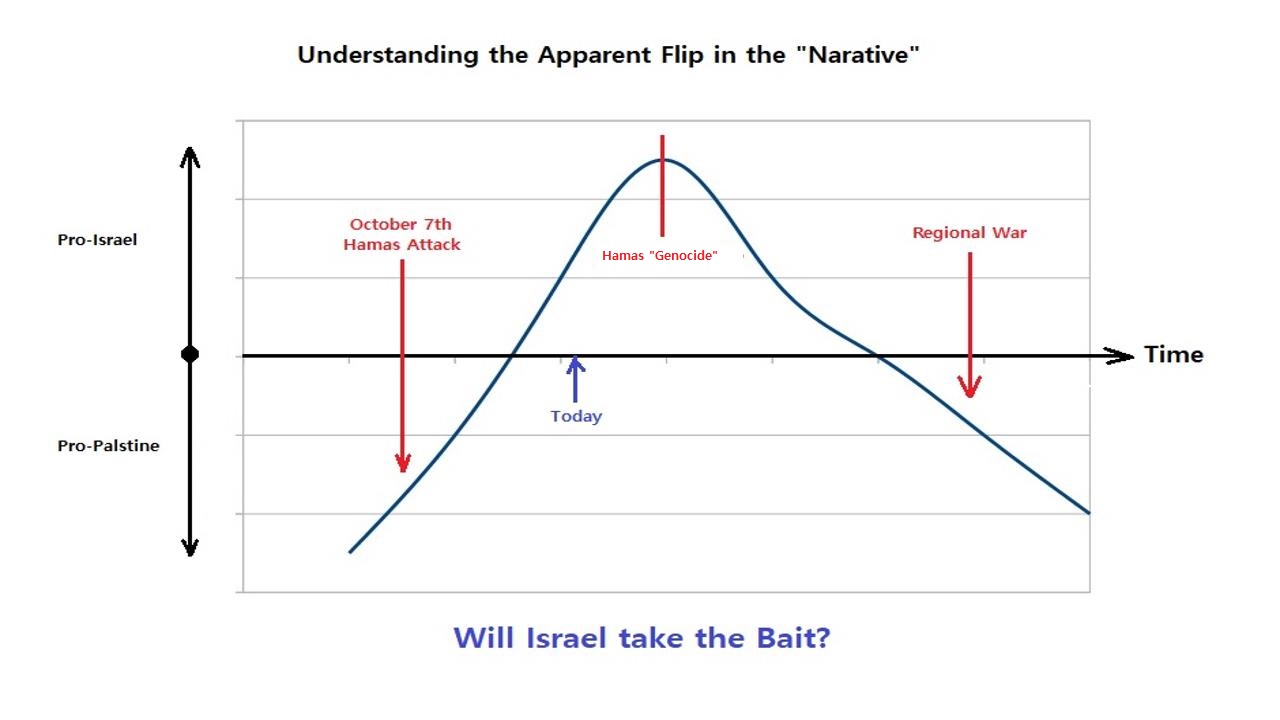
References:


Comments